The Bourne Again Shell Supports One-dimensional Array Variables
In itself, Linux is merely an operating system kernel; the kernel is a crucial component of the operating system, which facilitates I/O devices communicating with the software used by the user. Besides, it manages retentivity, CPU, and protects hardware and software from malfunctioning. The interface or software part that the user uses to collaborate with the hardware is chosen Command Line Interface (CLI) or a Vanquish.
Linux shell is a program with an interface that takes commands from the user, interprets them, and sends them to the kernel to perform a specified operation. Command Line Interface (CLI) is the minimalist way to collaborate with the hardware of the system. There are tons of commands for performing various functionalities, such every bit making a directory, moving a directory, creating a file, deleting a file, etc.
Shell is a basic command-line interpreter. It yields an interface between the user and the kernel. In Linux, there are many types of shells; a listing of commonly used shells are mentioned below:
- Bourne Shell
- Bourne Over again Trounce [Bash]
- C Beat out
- Korn Shell
- TC Shell
Different types of shells offer dissimilar capabilities. Ken Thompson introduced the first shell for Unix called Thompson Beat out. Bourne shell was 1 of the widely adopted shells developed past Stephen Bourne in 1977 at Bell Laboratories. Bourne Shell has an advanced version chosen Bourne Again Shell. Bourne Again Shell is besides called Bash. Bash was developed by Brian Fox that contained all the features of the Bourne shell but was it much more efficient.
Fustigate is the default shell from many Linux distributions, and the key features that distinguishBash fromshare are mentioned beneath:
- The powerful control editing feature
- Unlimited size of upshot history
- Introduction of aliases
- Unlimited size of arrays
Bash shell has many advanced features, including powerful editing and modification features, making it incredibly user-friendly.
The commands are the central part of Bash; commands tell the trounce what operation to perform. In general, the shell takes one control at a time, runs it, and so displays the output, which is as well called standard output in the shell. While executing a command, you cannot interact with the beat; the shell completes the performance before making itself bachelor for the next command. However, the execution of any command can be interrupted. The time of execution of control ultimately depends upon the type of role. For instance, if you lot are downloading a package, it might have longer than list the electric current working directory path.
Though the shell is designed to execute 1 command at a time, if you want to execute multiple commands to perform a specific task, Bash has a solution called Bash scripting.
- 1 Fustigate Scripting
- 2 What Are Arrays?
- 3 Applications of Arrays
- four Syntax of Arrays in Bash
- 5 Assigning Arrays in Fustigate
- 5.1 Assigning Arrays Through Loop
- v.2 Assigning Arrays From Strings
- 6 Types of Array in Bash
- 6.i Indexed Arrays
- six.2 Associative Arrays
- 7 Accessing an Assortment in Bash
- 7.one Displaying All Elements of an Array
- vii.2 Displaying Specific Chemical element of an Array
- 7.3 Accessing the Initialized Indexes of an Array
- 8 Modification of Arrays in Fustigate
- 8.ane Updating Elements
- 8.2 Adding Elements
- 8.3 Inserting Elements
- 8.iv Deleting Elements
- eight.5 Merging Arrays
- 8.6 Removing Gaps in Array Elements
- 9 Iterating Through the Assortment with Loops in Bash
- 10 Length of an Array in Bash
- 11 Accessing Associative Arrays in Bash
- 12 Bash Array Examples
- 12.ane Example 1: Reading a File Through Array
- 12.ii Example 2: Bubble Sorting in Bash
- 12.three Example three: Multidimensional Arrays in Fustigate
- 12.four Instance four: Formatting a Verse form in Bash
- Determination
i Bash Scripting:
A script is a fix of commands that tells the computer what information technology should exercise; a Bash script is also a set of commands that tells what Bash should perform. A Beat script is a text file that contains a sequence of commands to perform a particular task. Bash used Fustigate programming language, which like any other programming language, provides all the tools to perform logical operations such as assigning variables, conditional statements, loop structures, and arrays.
Equally mentioned above, Bash scripting is like any other programming language. To create a Bash program, you practise not need a powerful Integrated Development Environment (IDE) because information technology tin can be made on any simple text editor, whether it isnano,vim, or text editor that comes with the desktop environs.
To create a Bash script, open the text editor and reference the"/bin/bash" path using"#!" chosen hash-bang or shebang. The"/bin/fustigate"is the path of the Fustigate interpreter. The formatting in Bash scripting is very crucial; fifty-fifty a infinite tin cause errors. And shebang has to be on the superlative of the script. Blazon the script and save the file with the ".sh" extension. A basic"hello world" Bash script is shown beneath:
#! /bin/fustigate
echo "Hello Linux"

To run the script in the CLI, blazon"bash" and specify the path of the script.
Assigning variables in Bash scripting is simple. It does not need whatsoever data type; any grapheme, give-and-take, or string can be used as a variable:
variable_Name = [Value]
For instance:
#! /bin/bash
var="Hello Linux"
repeat $var

The "Hullo Linux" string is assigned to a variable chosen"var" in the above script. As a proper programming language, Bash as well supports provisional structures such as if-then , nested-if , and loop structures such as for-in and while-do .
A unmarried variable can concur one value that can be manipulated in the code. If you desire to define more than one variable of the same data blazon simultaneously, arrays are used. Moreover, arrays are also key elements of the Fustigate programming language. Arrays are a drove of elements that are identified by the index number. Arrays are essential when it comes to implementing data structure. Instead of typing multiple variables, arrays save time and are piece of cake on retention.
2 What Are Arrays?
The developers utilise many aspects of the Bash programming linguistic communication. There is plenty of data bachelor for other programming structures such every bit loops and conditional statements, but a structure that is not extensively covered is an array. The Bash array is a crucial construction of any programming language. It is implemented in the data structure.
Let's understand array with a real-life case:
- Postal service office box
- Pages of a book
- Chessboard
- A carton of eggs
The assortment is an arrangement of items. Therefore, every item is called an array if arranged in a way. For instance, egg cartons are the perfect example of the arrangement of items in 2D array manner. Eggs in the carton are elements where the box is an array. Similarly, pages in a book are bundled so the book would be called an array where pages would be elements.
Likewise, the contact numbers in our phones, songs, and an arrangement of apps on the dwelling house screen are likewise examples of an array.
Let's take an example of contacts in our phone, and the contact book is an example of an array where the contacts are elements of that array. Nosotros can manipulate the elements, such as adding a contact number and deleting a contact number.
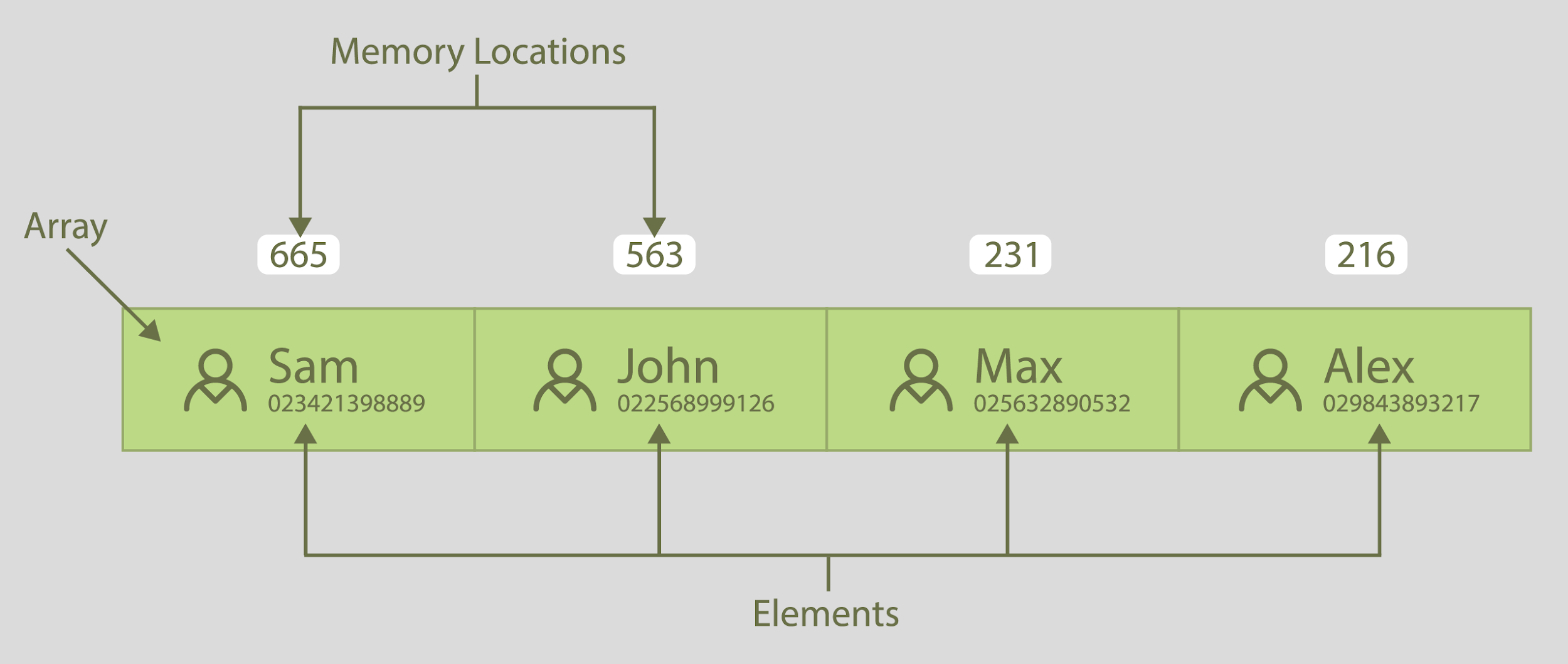
In the above demonstration, the contact numbers are elements of the array where the numbers above are memory locations.
When you lot visit an eCommerce site, the items y'all put in the shopping cart are likewise an instance of an array, since y'all can add items to the shopping cart and remove them.
A variable that tin store multiple variables is called an assortment. There is no limit when it comes to assigning a number of variables in an assortment. Array elements are referenced by the index number, which usually starts with zippo. The array is mainly used in implementing information structure, which is an arroyo to organize and manage data effectively. Let'south visualize an assortment as a container with multiple compartments, as shown in the image below:
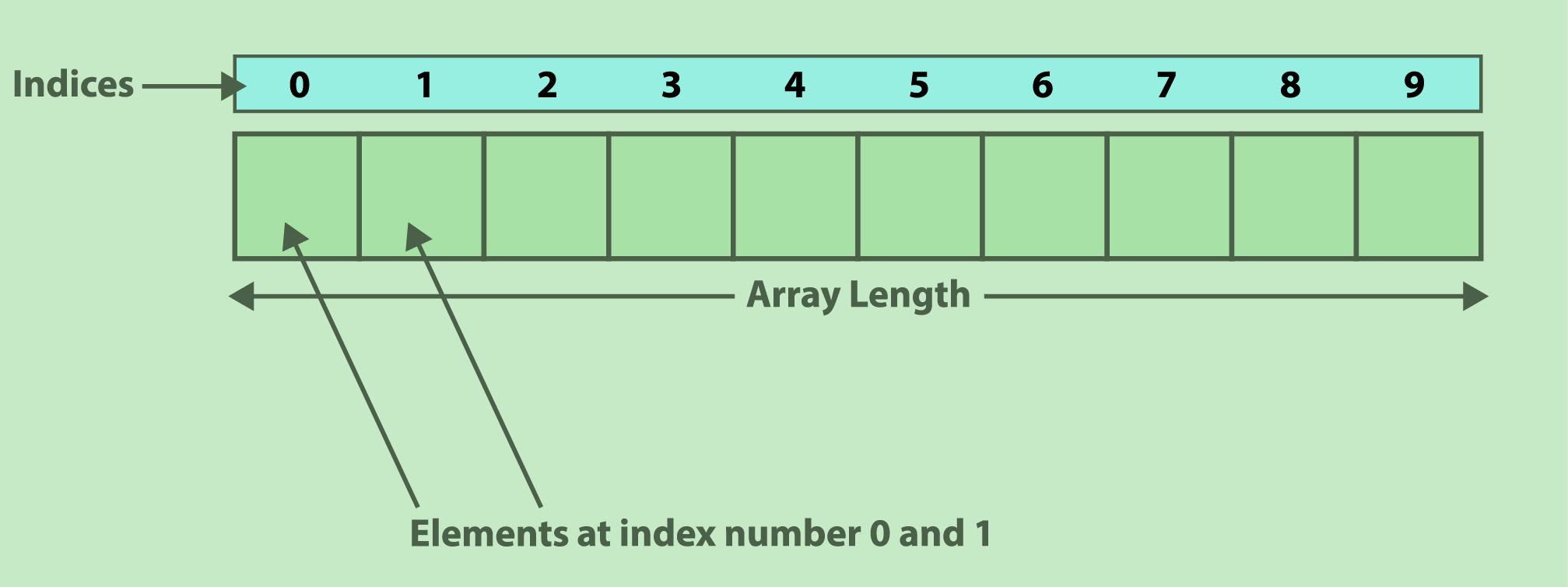
There are x compartments in the above demonstration, and then the length of the array would exist 10. The get-go compartment number would be 0 and the terminal would be 9. The compartments can also exist termed as the elements of the assortment.
Instead of defining multiple variables 1 by ane, arrays help them define them at once; that is an efficient way of assigning variables in programming.
3 Applications of Arrays:
Arrays are such a powerful utility that they can be used in many scientific calculations. Arrays in any programming language are much more functional than other structures. Some notable implementation of arrays are mentioned below:
- Arrays are used to manage multiple variables with the same proper noun.
- Arrays tin be used in vectors, where vectors are typically one-dimensional arrays that are extensively used in car learning.
- Arrays are also used in implementing stacks, and stacks comport similar a real pile of physical objects.
- Arrays are also implemented in queues, deques, and hash tables.
- Matrices, which are a rectangular assortment of elements, are also implemented using arrays.
- Graphs in many programs are drawn using lists which is besides any implementation of assortment.
- Many algorithms, such equally CPU scheduling algorithms and sorting algorithms, are implemented using the array.
- Arrays are also used in in-program dynamic memory allocation.
- Arrays are also used in speech processing.
- Dissonance removing filters are likewise using arrays.
The above implementations of arrays clearly prove the potential of the arrays information blazon.
iv Syntax of Arrays in Bash:
Bash comes with the support of both indexed array (ane-dimensional array) and associative arrays, which will exist discussed in the later on section. A typical syntax of assigning array in Bash is mentioned below:
name_of_array[subscript]=value
Since arrays are collections of objects, the object number in the array is called index number or subscript. Subscripts bespeak the position of the object in the array. For instance, to assign or alter the value of x thursday object in the array, the syntax would be:
The "declare" keyword can also exist used to declare an array:
To declare an associative array:
The syntax of compound consignment of an array is:
name_of_array=(value1 value2 …)
Any of the previously mentioned methods can be utilized to state arrays in Bash scripting.
5 Assigning Arrays in Fustigate:
Arrays in Bash scripting can be assigned in diverse ways. The simplest fashion to assign an assortment in Fustigate scripting is assigning a gear up of values with infinite in round brackets to a variable every bit demonstrated below:
The Fustigate arrays tin can have different types of elements. To assign array with cord elements:
my_array=(jan feb mar april)
To explicitly assigning an array with indices:
my_array=( [ 0 ]='jan' [ 1 ]='feb' [ 2 ]='mar' [ three ]='apr')
To assign the array with index, blazon the name of the array, mention the alphabetize in the foursquare brackets, "[index_number]" and assign a value to it:
my_array[ 0 ]='jan'
my_array[ i ]='feb'
The array can too be declared with the "declare" keyword. The options"-a" and"-A"is used to declare indexed and associative arrays, respectively:
declare -a my_array
my_array[ 0 ]='january'
my_array[ i ]='feb'
String values are used as the index in associative arrays:
declare -A my_array
my_array[first]='jan'
my_array[2nd]='february'
Or:
my_array=( [offset]='jan' [second]='feb' [3rd]='mar' [fourth]='apr')
The array can also be created from the output of other commands.
For instance, the"seq" command is used to create a list of numbers:
5.1 Assigning Arrays Through Loop:
Array can likewise be assigned through loops, for example:
#! /bin/bash
while
read
practise
my_array[ $n ]=$REPLY
permit n++
done < < ( seq one 6 )
echo "Array elements are:" ${my_array[@]}
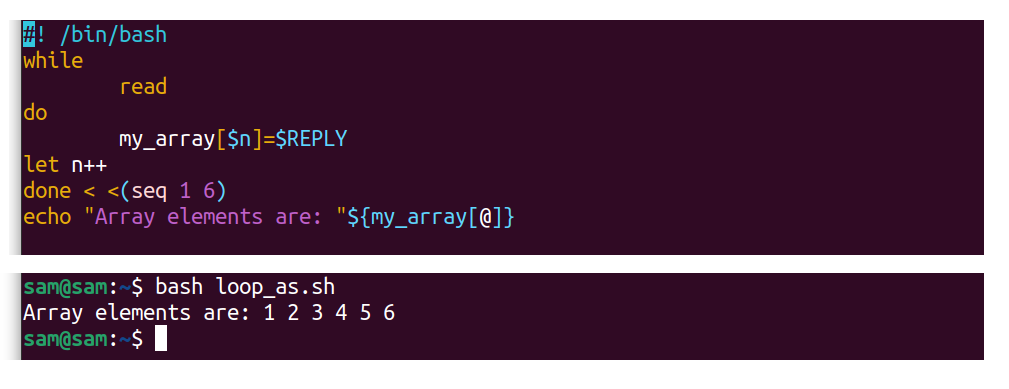
The"$REPLY" is the special variable and equals the current input.
5.2 Assigning Arrays From Strings:
An entire string tin can also be assigned as an array. For example:
my_array_string="Hello this is Linux"
my_array=( ${my_array_string// / } )
In the in a higher place script, the delimiter is a "space". A delimiter is a character that individualizes the text string, such as slashes, commas, colons, pipes, and even spaces. In the next instance, the delimiter is dash:
my_array_string="Hello-this-is-Linux"
my_array=( ${my_array_string//-/ } )
Permit's implement it in Bash scripting:
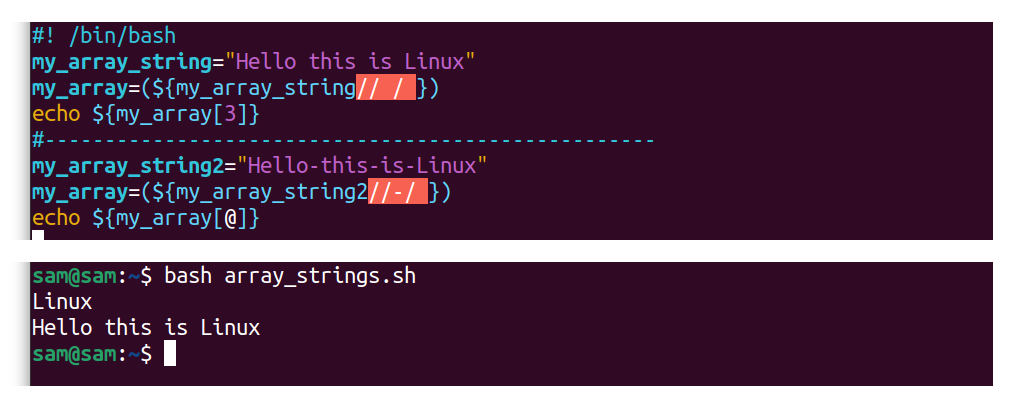
#! /bin/bash
my_array_string="Hello this is Linux"
my_array=( ${my_array_string// / } )
echo ${my_array[iii]}
#--------------------------------------
my_array_string2="Hullo-this-is-Linux"
my_array=( ${my_array_string2//-/ } )
echo ${my_array[@]}
half dozen Types of Array in Bash:
There are many means and approaches to utilize an array. In Bash, there are two types of chief arrays:
- Indexed arrays
- Associative arrays
6.one Indexed Arrays:
Indexed arrays are the principal form of an array that stores elements referenced through an index number starting from 0. An example of an indexed assortment in Bash scripting is mentioned beneath:
Or arrays tin can also be declared using the "declare" keyword:
my_array[ 0 ] = "First Detail"
my_array[ ane ] = "Second Item"
In the above case,"array" is a variable"a, b, c, and d" are the elements of the array. The array's length would exist 4, and the index number of the"a" chemical element would be on the zeroth alphabetize and"d" on the third index.
half-dozen.2 Associative Arrays:
Associative arrays are the arrays that use cord as index. In other words, the array index in associative arrays is in named form. Associative arrays are declared in Bash using the "declare" keyword.
declare -A my_array
my_array[one] = "Start Item"
my_array[two] = "Second Particular"
Associative arrays are non part of Fustigate before they are included in version 4. To identify which version are you using, utilise the command given below:
If the version is iv or to a higher place, then you can use associative arrays. To declare associative assortment"-A" option is used explicitly:
Elements can too be initialized one by one:
my_array[month1]="january"
my_array[month2]="feb"
Any string or prepare of characters are used to declare an associative array:
my_array[ "this is a string" ]="Howdy Linux"
It is important to note that the cord in the array indexes, as mentioned above, is containing space. Another way of initialization of associative arrays are given beneath:
my_array=( [month1]=jan [month2]=feb [month3]=mar)
Currently, Fustigate does non support multidimensional arrays. However, dissimilar methods tin can emulate multidimensional arrays, which tin be constitute in the examples section.
7 Accessing an Assortment in Bash:
Like all other programming languages, arrays in Bash are besides accessed through alphabetize numbers. Let'due south understand it through an example:
my_array=(january feb mar apr)
echo ${my_array[1]}
The"echo"is a Bash command that prints the standard output in the command-line interface (CLI). In the above example, the"echo" command is printing the particular on the first alphabetize of the array"my_array". The"feb" will exist printed on the standard output since the index number of"february" isi.
7.1 Displaying All Elements of an Array:
To brandish all the elements of the assortment quoted separately, follow:
To display all the elements as a single quote string, use:
vii.ii Displaying Specific Chemical element of an Array:
To display any element of the array, use:
Replace the"x"with the index number of the element y'all want to display. For case, to print the third chemical element of the array, utilise:
Print final element of an array through the subscript expansion method:
To print the last element via subscript syntax, use:
To print a range of elements, use the syntax mentioned beneath:
Where"x" is the first index number, and the"y" would exist the last alphabetize number. For instance, to display elements from alphabetize"0" to"2", use:
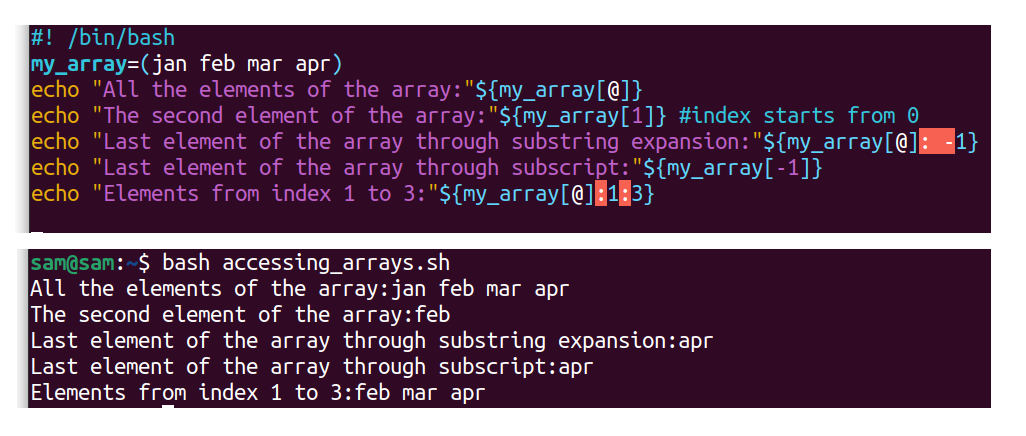
The above command volition print three elements from index 0 to 2. All the operations for accessing arrays are demonstrated in the following image:
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(jan feb mar april)
echo "All the elements of the array:" ${my_array[@]}
echo "The second chemical element of the array:" ${my_array[one]} #index starts from 0
echo "Last chemical element of the array through substring expansion:" ${my_array[@]: -1}
echo "Last element of the array through subscript:" ${my_array[-1]}
echo "Elements from index 1 to 3:" ${my_array[@]:1:three}
7.3 Accessing the Initialized Indexes of Array:
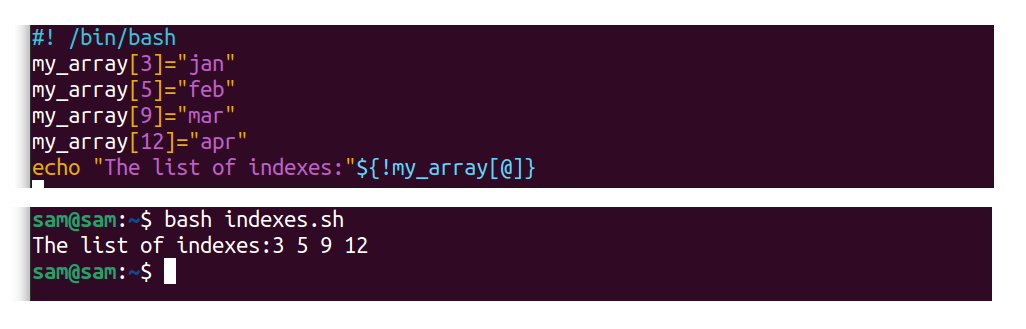
The alphabetize of an assortment is the fundamental element while programming. To get the index number, apply:
#! /bin/bash
my_array[ 3 ]="jan"
my_array[ five ]="february"
my_array[ 9 ]="mar"
my_array[ 12 ]="mar"
echo "The list of indexes:"${!my_array[@]}
viii Modification of Arrays in Bash:
One of the benefits of using arrays is that whatever array element tin can easily exist accessed and modified. Arrays in Bash have various ways to change; all the methods are mentioned below:
8.ane Updating Elements:
To update a particular element in an array, follow the following syntax:
my_array[ <index_number> ]=value
For example:
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(jan february mar apr)
my_array[ 2 ]="may"
echo "The updated chemical element:"${my_array[@]}
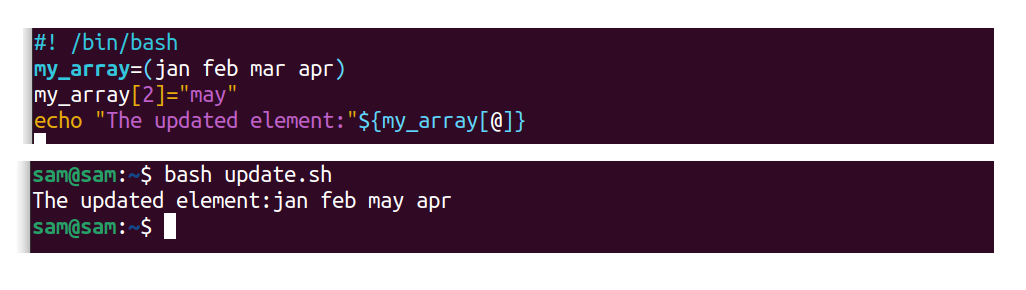
In the to a higher place example, the element on the 2nd alphabetize, which is"mar" will be replaced by"may".
8.two Adding Elements:
To add elements to the terminate of an array:
To add an element at the starting of an array:
my_array=('dec' ${my_array[@]} )
Let's implement it in a Bash script:
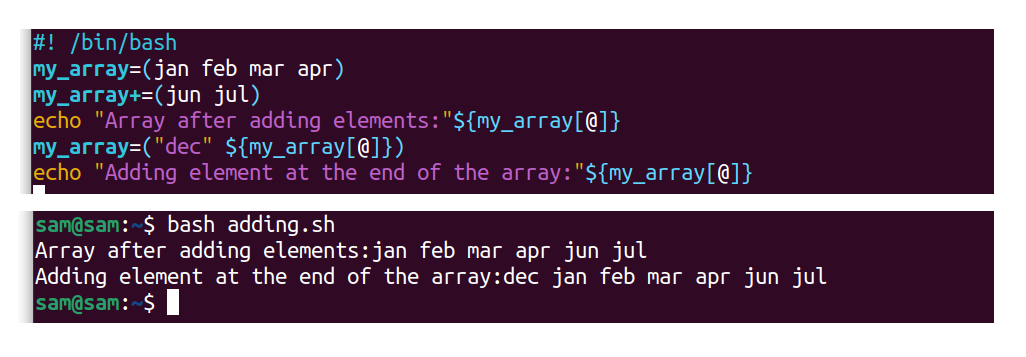
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(january feb mar april)
my_array+=(jun jul)
repeat "Assortment after adding elements:" ${my_array[@]}
my_array=( "dec" ${my_array[@]} )
echo "Calculation chemical element at the stop of the array:" ${my_array[@]}
8.3 Inserting Elements:
To insert an chemical element at a specific index, follow:
my_array(jan february mar april)
i=2
my_array=("${my_array[@]:0:$i}" "aug" "${my_array[@]:$i}")
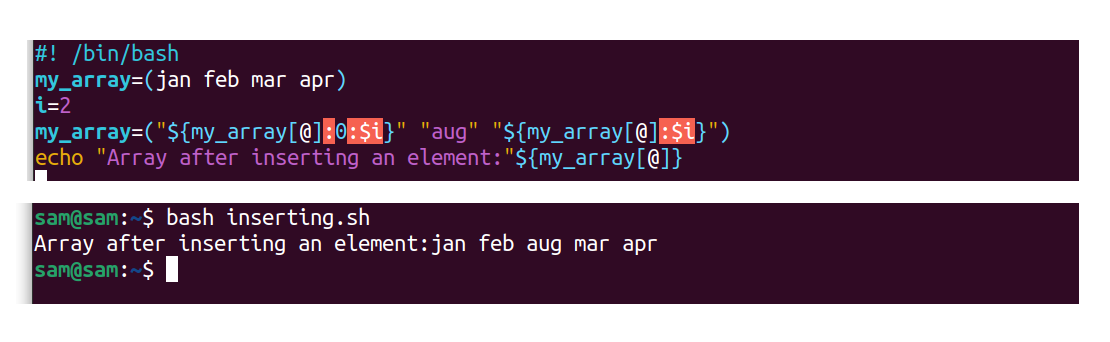
The above example is inserting the element "aug" on the second index of the assortment(my_array) and shifting the following elements to the next indexes. The elements "mar" and "apr" will exist shifted to index iii and four respectively:
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(jan feb mar april)
i=2
my_array=( "${my_array[@]:0:$i}" "aug" "${my_array[@]:$i}" )
echo "Assortment after inserting an element:" ${my_array[@]}
8.four Deleting Elements:
In Bash arrays, elements tin be deleted using the "unset" command. For example, to remove all the elements of an array, apply:
my_array=(january feb mar apr)
unset my_array
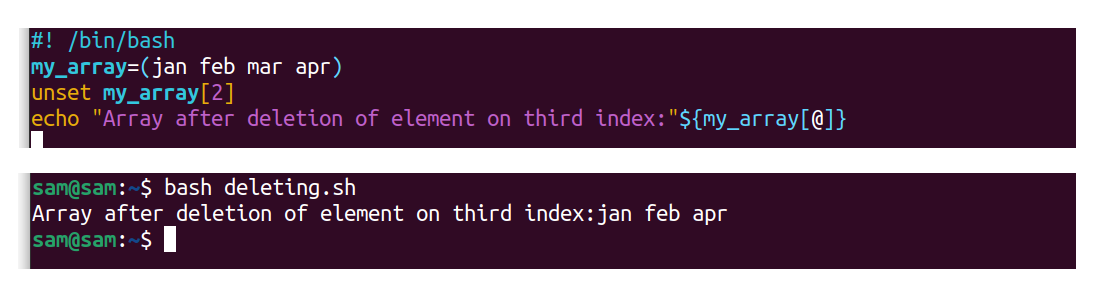
The"unset"is the built-in command to delete the declared variables. To unset a specific chemical element in an array, utilize:
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(jan feb mar apr)
unset my_array[ 2 ]
echo "Array after deletion of element on 3rd index:"${my_array[@]}
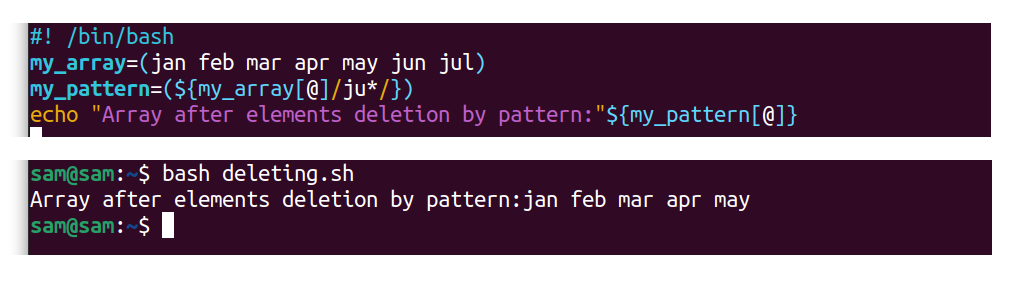
Elements can as well be removed using the "pattern" command:
my_pattern( ${my_array[@]/ju*/} )
The elements that start with"ju" will exist removed from the array, every bit shown in the output of the following script:
#! /bin/fustigate
my_array=(jan feb mar april may jun jul)
my_pattern( ${my_array[@]/ju*/} )
echo "Array after elements deletion by design:"${my_pattern[@]}
8.5 Merging Arrays:
To merge two arrays employ:
my_array=( ${my_array1[@]} ${my_array2[@]} )
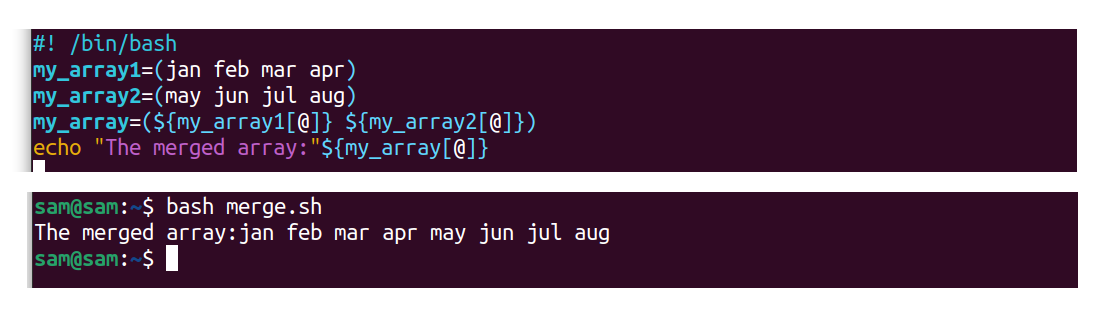
Let'southward merge 2 arrays in Fustigate:
#! /bin/bash
my_array1=(jan february mar apr)
my_array2=(may jun jul aug)
my_array=( ${my_array1[@]} ${my_array2[@]} )
echo "The merged array:" ${my_array[@]}
8.6 Removing Gaps in Assortment Elements:
To remove the unintended gaps in the assortment and re-indexing array employ:
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(jan feb mar april)
my_array2=( ${my_array[@]} )
echo "Assortment later on removing gaps:"${my_array2[@]}
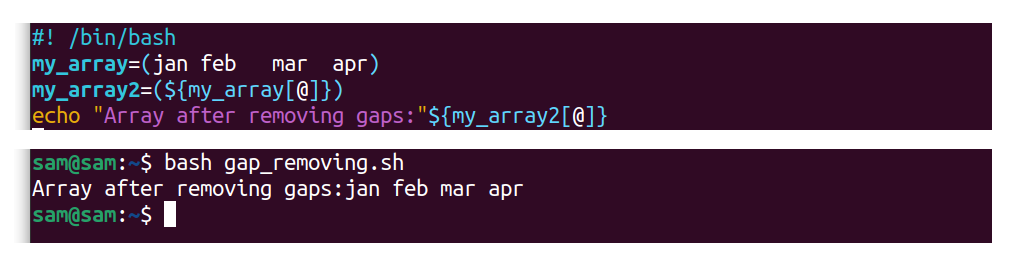
In the to a higher place demonstration, elements of "my_array" accept gaps in them.
9 Iterating Through the Assortment with Loops in Fustigate:
In that location are diverse ways to access an array; either yous tin can admission them explicitly by typing every chemical element, or you can loop through the elements of the assortment. Permit's sympathize it through an example:
my_array=(e1 e2 e3 e4 e5 e6)
First, use the "for…in" loop:
for i in ${my_array[@]}
do
echo $i
done
C is a widely used programming language. Luckily in Bash, y'all tin besides employ the C language style "for" loop, which is also termed equally the archetype loop:
for ( ( i=0;i< ${#my_array[@]};i++) );
do
echo ${my_array[i]}
done
Arrays can also be accessed through while loop:
i=0
while [ $i -lt ${#my_array[@]} ];
do
repeat my_array[ $i ]
i=$( (i+1 ) )
washed
Instead of"-lt", the less than sign "<" can also be used,the in a higher place loop tin can also exist written every bit:
i=0
while ( ( $i < ${#my_array[@]} ) );
do
echo my_array[ $i ]
( (i++) )
done
The until loop tin also be used to iterate through the arrays:
i=0
until [ $i -ge ${#my_array[@]} ];
practice
echo ${my_array[i]}
i=$( (i+1 ) )
done
In numerical format:
i=0
until ( ( $i < ${#my_array[@]} ) );
do
repeat ${my_array[i]}
i=$( (i+one ) )
done
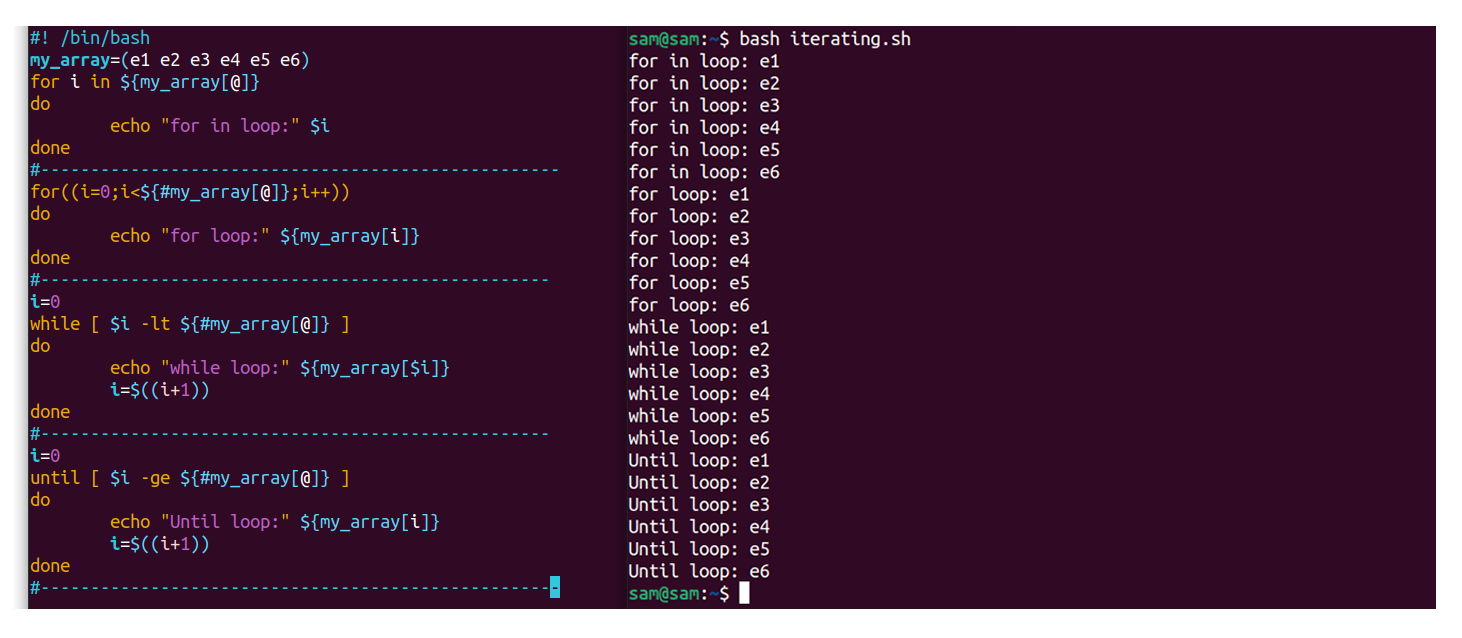
The script of implementation of all the loop structures in Bash is mentioned below:
#! /bin/fustigate
my_array=(e1 e2 e3 e4 e5 e6)
for i in ${my_array[@]}
practice
echo "for in loop:" $i
done
#----------------------------------------------------
for ( ( i=0;i< ${#my_array[@]};i++) )
do
echo "for loop:" ${my_array[i]}
washed
#---------------------------------------------------
i=0
while [ $i -lt ${#my_array[@]} ]
practise
echo "while loop:" ${my_array[$i]}
i=$( (i+one ) )
washed
#---------------------------------------------------
i=0
until [ $i -ge ${#my_array[@]} ]
do
echo "Until loop:" ${my_array[i]}
i=$( (i+1 ) )
done
#----------------------------------------------------
ten Length of an Array in Bash:
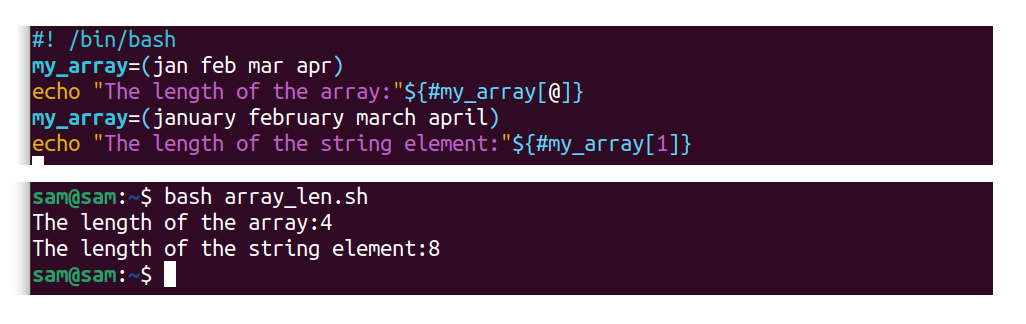
Knowing the length of the array is very important when working with arrays. To identify the length of an array, use:
my_array=(jan feb mar apr)
echo ${#my_array[@]}
The character "#" is used before the assortment proper name.
If the elements of an assortment are in a cord format, and so to know the length of a cord element in an array, use:
my_array=(january february march apr)
echo ${#my_array[1]}
The above commands will output the length of the second chemical element of the array, which is eight, since "feb" is eight characters long.
#! /bin/bash
my_array=(jan feb mar apr)
echo "The length of the array:" ${#my_array[@]}
my_array=(january february march april)
echo "The length of the string chemical element:" ${#my_array[one]}
11 Accessing Associative Arrays in Bash:
Accessing the associative arrays are like to accessing the indexed arrays. The only difference is that in associative arrays the index is cord:
declare -A my_array=( [month1]=jan [month2]=february [month3]=mar)
repeat ${my_array[month1]}
To list the indices of associative arrays, utilize:
To brandish the values of the assortment, use:
Iterate through the associative arrays:
my_array=( [month1]=jan [month2]=feb [month3]=mar [month5]=apr)
for i in ${!my_array[@]} ;
do
echo my_array[ $i ]
done
To count the elements of the associative arrays, use:
my_array=( [month1]=jan [month2]=feb [month3]=mar [month5]=april)
echo { #my_array[@]}
All the previously mentioned structures are implemented in the script given below:
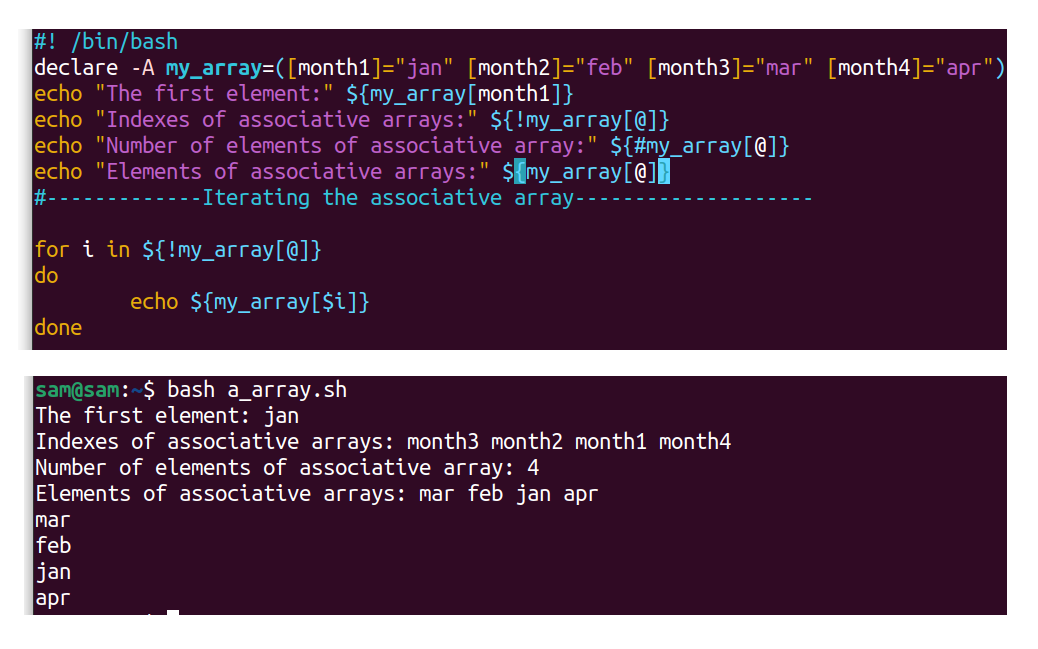
#! /bin/bash
declare -A my_array=( [month1]="jan" [month2]="february" [month3]="mar" [month4]="apr" )
echo "The outset element:" ${my_array[month1]}
repeat "Indexes of associative arrays:" ${!my_array[@]}
echo "Number of elements of associative array:" ${#my_array[@]}
echo "Elements of associative arrays:" ${my_array[@]}
#-------------Iterating the associative array-------------------
for i in ${!my_array[@]}
practice
repeat ${my_array[$i]}
done
| Action | |
| echo $array[@] | To print all elements of an array |
| echo $!assortment[@] | To print the all indexes of an array |
| echo $#array[@] | To print the length of an assortment |
| echo $array[ten] | To impress a specific element of an assortment by index "x" |
| array[x]=value | To insert/supplant an element to a specific index of an assortment |
| unset array[x] | To remove an element at a specific index |
12 Bash Array Examples:
Bash arrays are the information construction and are very useful for handling the collection of variables. Arrays take various uses in programming. Let's further elaborate on the uses of arrays through examples:
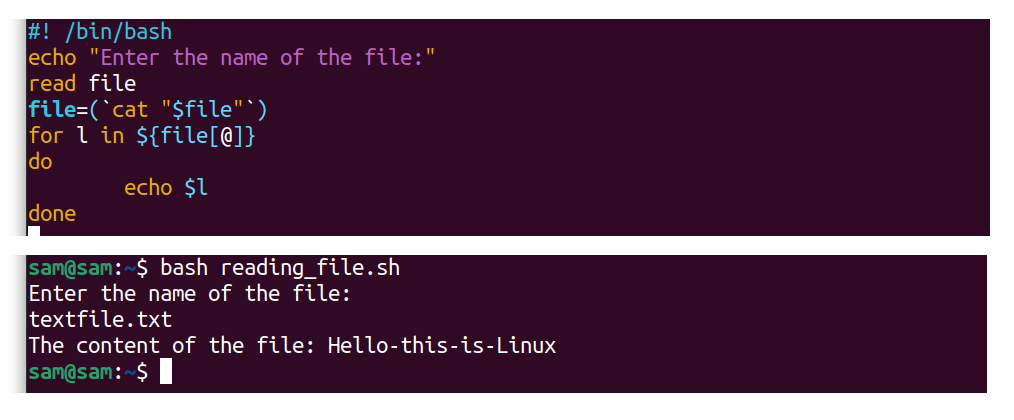
12.one Example 1: Reading a File Through Array:
To read a file, we need to create a file first. At that place are diverse ways to create a file in Linux, for example, using a redirection operator, true cat, or bear on command. The created file tin be edited in nano or vim editor.
I have created a file in"nano" and saved it with the name of"my_file.txt". To read file, apply:
$cat my_file
#! /bin/bash
echo "Enter the name of the file"
read file
file=( ` cat "$file"` )
for l in ${file[@]}
do
echo $l
done
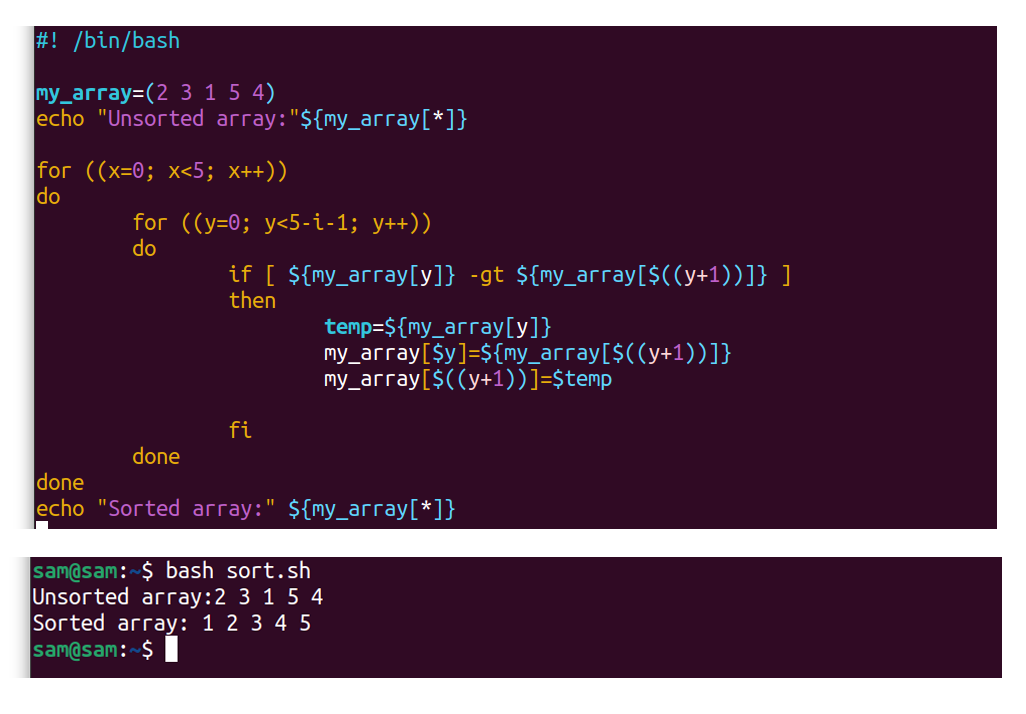
12.ii Example 2: Bubble Sorting in Bash:
Sorting is used to manage the data, and it is one of the well-known techniques in programming to make the algorithm functionality more efficient such equally search algorithm. Bubble sorting, which is besides known as sinking sorting, is one of the piece of cake-to-understand sorting approaches. Bubble sort steps through the provided array list, compare the assortment elements, swap the chemical element in the temporary variables and repeat the task until the array is in order. An example of bubble sorting in bash is given below:
#! /bin/bash
my_array=( 2 3 one five 4 )
echo "Unsorted assortment:" ${my_array[*]}
for ( ( 10=0; 10< 5; x++) )
do
for ( ( y=0; y< 5-i-1; y++) )
practise
if [ ${my_array[y]} -gt ${my_array[$((y+1))]} ]
then
temp=${my_array[y]}
my_array[ $y ]=${my_array[$((y+ane))]}
my_array[$( (y+one ) ) ]=$temp
fi
done
washed
echo "Sorted array:" ${my_array[*]}
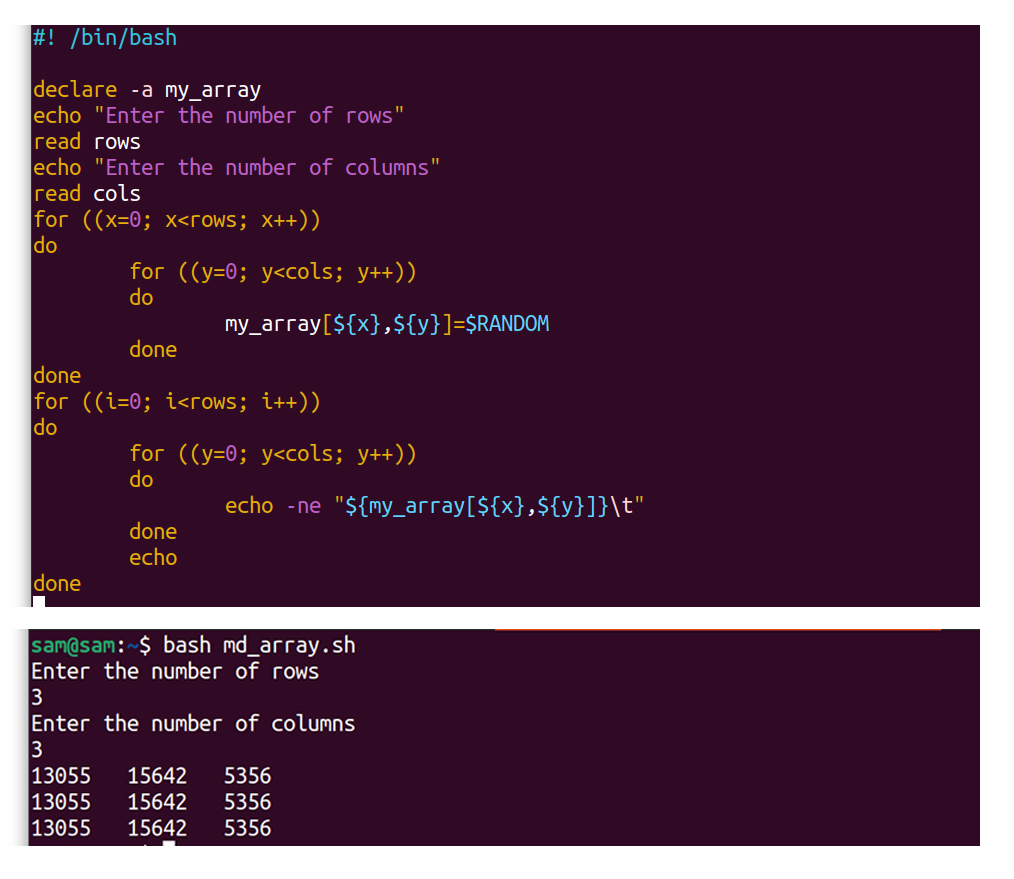
12.iii Example three: Multidimensional Arrays in Bash:
Multidimensional arrays are not the official part of the Bash programming language. But Bash supports the major programming structures, most importantly loops. Multidimensional arrays can easily be simulated using "for" loops:
#! /bin/bash
declare -a my_array
echo "Enter the number of rows"
read rows
echo "Enter the number of columns"
read cols
for ( ( 10=0; ten<rows; x++) )
do
for ( ( y=0; y<cols; y++) )
do
my_array[ ${x},${y} ]=$RANDOM #Assigning a random number
done
done
for ( ( i=0; i<rows; i++) )
exercise
for ( ( y=0; y<cols; y++) )
do
echo -ne "${my_array[${ten},${y}]}\t"
done
echo
washed
The higher up code takes rows and columns as input from the user and then generates a pseudo-random number from 0-32767 .
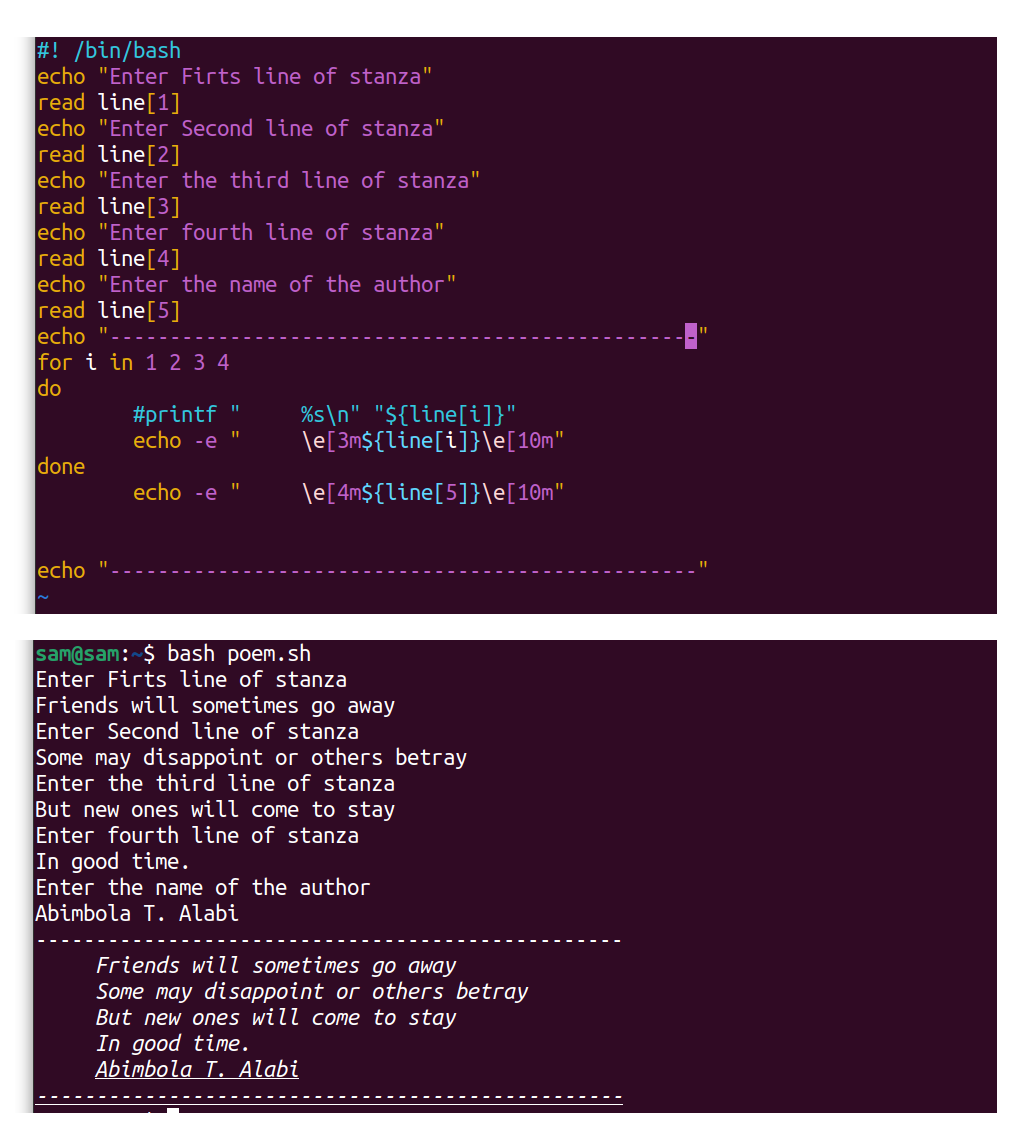
12.4 Example 4: Formatting a Poem in Bash:
The following example is another implementation of the array. The script is taking stanza lines as input from the user, format them, and print the unabridged stanza in the standard output:
#! /bin/fustigate
repeat "Enter First line of stanza"
read line[ ane ]
repeat "Enter Second line of stanza"
read line[ ii ]
repeat "Enter third line of stanza"
read line[ three ]
echo "Enter quaternary line of stanza"
read line[ 4 ]
repeat "Enter the proper noun of the author"
read line[ v ]
for i in one 2 iii 4 #Getting four lines of the stanza
do
echo -east " \eastward[3m${line[i]}\e[10m" #Making the text italic
done
repeat -e " \e[4m${line[5]}\e[10m" #Underlining the text
Conclusion:
The assortment is ane of the critical structures in any programming linguistic communication. It allows to shop different elements of the same information type in a single variable, and those elements can be accessed through alphabetize position. Arrays are used in data structure, hash tables, linked lists, or search trees.
Linux is growing, though it has a very pocket-size desktop computer market. The principal source to interact with the Linux kernel is the shell. Shell is an interface that assists a user to communicate with the Linux organisation's kernel. There are diverse types of shells, but the widely adopted beat out is the Bourne Once again Shell, likewise known as Fustigate. Bash takes command as input from the user and interprets information technology for the kernel to perform a task.
Similarly, to execute multiple commands or perform a specific task, Bash scripting is used. Bash scripting is also called shell scripting and uses Fustigate programming linguistic communication, which is no less than any other scripting language. Like any other programming language, Fustigate includes everything such as variable defining, provisional statements, and loops. The array is an important data structure that is used to manage the data.
The office of arrays in Bash scripting is the same every bit other programming languages. But still, arrays are not as advanced in Bash as other scripting or programming languages.
Bash offers two types of arrays, indexed array and associative arrays. Associative arrays were introduced in the fourth version of bash. In the indexed array, the indexes are numeric, whereas, in associative arrays, indexes can be strings. The indexes of associative arrays are besides called keys.
Bash provides various array modification options such equally inserting an element, deleting an element, replacing an chemical element, and accessing an element at a specific index. Fustigate arrays can have multiple uses, playlists in music players, and contacts in your contact listing are examples of usage of an array. Moreover, arrays can be used as information direction, stacks, queues, heaps, etc.
In Fustigate, arrays are not as powerful as in other programming languages. At that place are multiple reasons: Bash is non an object-oriented programming language, the syntax is hard to learn, slow execution fourth dimension, and vulnerable to errors. Additionally, it does not back up multidimensional arrays.
Despite that, arrays can exist useful in performing various tasks such equally parameter sweep, log alerting while performing cronjobs, and many other programming logic.
Source: https://linuxhint.com/bash-arrays-tutorial/
0 Response to "The Bourne Again Shell Supports One-dimensional Array Variables"
Post a Comment